Ongoing Projects
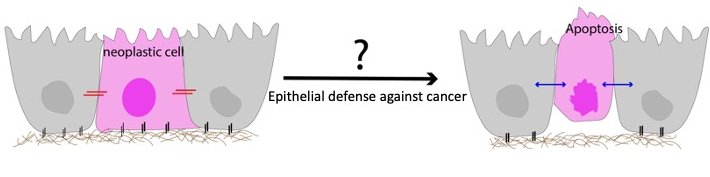
EDAC
Epithelial Defense Against Cancer
In pathological situations, cancer is a mass of over-proliferating cells growing in the space of our host epithelial tissues. In Epithelia, elimination of oncogenic cells via cell competition is a defence mechanism against cancer- Epithelial defence against cancer (EDAC). How is EDAC impaired and how do cancer cells gain the competitive advantage over host epithelial tissues? Can we generate novel anticancer therapies which enhances our body’s defence mechanism against cancer?
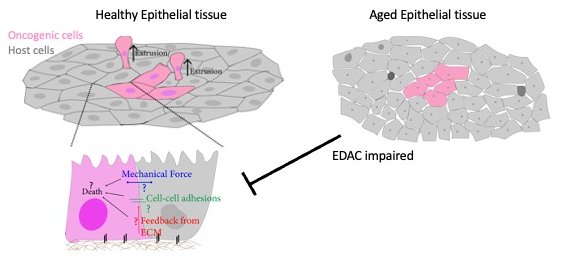
Ageing and cancer
Understanding correlation between age and cancer
Aging is considered as a pro-tumorigenic state and constitutes the single most important risk factor for cancer development. The causative relation between ageing and cancer is majorly considered to be the accumulation of oncogenic mutations over long period of time. However, an alternative, but not mutually exclusive hypothesis is possible i.e. aging influence the overall tissue mechanics and subsequently impair our tissue’s defence mechanism against cancer.
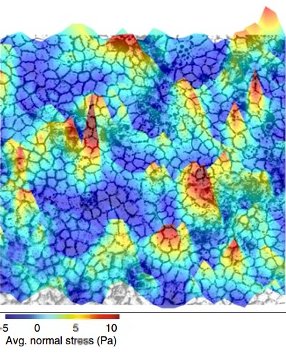
Heterogeneity and epithelial function
The restlessness
Recent technological and computational advances have allowed us to describe behaviour of epithelia using mesoscale physical principles. In such description, similar to glassy solids or dense particulate matter, epithelial cells are shown to display characteristics of dynamic heterogeneity. In addition to this physical heterogeneity, epithelial cell biology reveals an intrinsic cellular heterogeneity arising from variations in gene expression pattern. Physical and biological heterogeneity is likely to be interactive and interdependent. But How? How do they crosstalk to regulate tissue function such as wound healing and epithelial defence against cancer?